Nerve and Continence preserving Robotic Radical Prostatectomy for Cancer Prostate
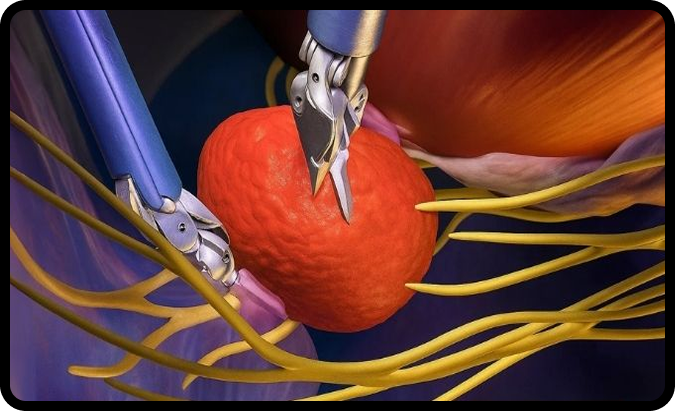
Overview
- A cutting-edge, minimally invasive robotic surgery performed to remove the prostate gland affected by cancer.
- Uses the da Vinci Robotic System for superior precision, stability, and 3D magnification.
- Designed to achieve complete cancer removal while protecting:
- Neurovascular bundles (responsible for erections)
- Sphincter muscles (responsible for urinary control)
- Pelvic floor support structures
- Neurovascular bundles (responsible for erections)
- Gold-standard treatment for localized early-stage prostate cancer.
What Does “Nerve & Continence Preservation” Mean?
Nerve Preservation
- Targeted protection of the penile neurovascular bundles that control erectile function.
- Helps maintain natural erections post-surgery.
- Performed as:
- Bilateral nerve-sparing
- Unilateral nerve-sparing
- Partial nerve-sparing—based on cancer involvement.
Continence Preservation
- Focused on maintaining urinary control mechanisms by preserving:
- External urinary sphincter
- Bladder neck
- Supportive pelvic structures
- Distal urethra length
- External urinary sphincter
- Uses special reconstructive techniques to enable faster return to continence.
Indications for the Procedure
- Localised prostate cancer (Stage T1–T2).
- Patients with:
- Rising PSA levels
- Cancer found in biopsy
- MRI showing organ-confined disease
- Good sexual function pre-surgery
- Suitable for men seeking functional preservation along with cancer cure.
- Rising PSA levels
Preoperative Evaluation
- Detailed clinical examination.
- PSA monitoring.
- MRI prostate for mapping cancer location and nerve involvement.
- Complete blood tests and fitness evaluation.
- Counselling regarding:
- Fertility
- Sexual function outcomes
- Continence recovery timeline
- Fertility
- Prehabilitation:
- Pelvic floor exercises
- Diet and lifestyle modifications
- Pelvic floor exercises
Advantages of Robotic Surgery (In This Procedure)
Technical Advantages
- 10x magnified HD 3D vision
- Enhanced dexterity with wristed robotic instruments
- Tremor-free surgical movements
- Better access to deep pelvic areas
Clinical Advantages
- Less blood loss
- Fewer complications
- Minimal tissue trauma
- Smaller scars
- Shorter hospital stay
Functional Advantages
- Higher success in nerve preservation
- Earlier urinary continence
- Better chances of sexual function recovery
- Faster return to regular activities
Step-by-Step Surgical Procedure
- Patient Positioning & Anaesthesia
- Procedure performed under general anaesthesia.
- Patient placed in steep Trendelenburg position for optimal pelvic access.
2. Port Placement
- 5–6 small incisions (8–12 mm) created for robotic arms and camera ports.
- Abdominal cavity inflated with CO₂ to provide working space.
3. Robotic Docking
- da Vinci robot is docked to the surgical ports.
- Surgeon controls the console from a separate unit.
4. Dissection Phase
- Precise separation of prostate from surrounding tissues.
- Identification of key structures:
- Bladder neck
- Seminal vesicles
- Neurovascular bundles
- Bladder neck
- Urethral sphincter
5. Nerve – Sparing Stand
- Gentle, atraumatic dissection of nerves from the prostate capsule.
- Energy sources used minimally to avoid thermal injury.
- Nerve bundles left intact as much as possible.
6. Continence-Sparing Reconstruction
- Bladder neck preservation (whenever anatomically safe).
- Reconstruction of posterior musculofascial support (Rocco stitch).
- Preservation of maximum sphincter length.
- Vesicourethral anastomosis—precision suturing connecting bladder to urethra.
7. Prostate Removal
- Prostate placed in an endobag and removed via one port.
- Lymph nodes removed if indicated (extended pelvic lymph node dissection).
8. Completion
- Ports removed; incisions closed with minimal sutures.
- Foley catheter placed for temporary urinary drainage.
Postoperative Care & Recovery
Hospital Stay
- Usually discharged in 24–48 hours.
Catheter Management
Catheter removed after 7–10 days following healing confirmation.
Pain & Mobility
- Minimal pain due to small incisions.
- Early mobilization encouraged from Day 1.
Diet
- Clear liquids on the same day; soft diet next morning.
Activity
- Return to office work in 2–3 weeks.
- Heavy lifting avoided for 4–6 weeks.
Outcomes Expected
Cancer Control
- High cancer cure rate with negative surgical margins.
- Accurate removal of cancerous tissues.
Urinary Continence
- Majority regain continence within:
- 1–2 weeks (early responders)
- 6–12 weeks (typical)
- 3–6 months (delayed responders)
- 1–2 weeks (early responders)
- Continence preservation techniques improve outcomes significantly.
Sexual Function
- Recovery timeline depends on:
- Age
- Preoperative sexual function
- Grade of nerve-sparing
- Age
- Robotic nerve-sparing increases chances of recovering natural erections.
Possible Risks & Complications
- Temporary urinary leakage
- Erectile dysfunction (varies per patient)
- Rare injury to rectum or surrounding tissues
- Infection or bleeding
- Scar tissue formation causing narrowing (stricture)
- Lymphocele formation after lymph node removal
- Very rare: blood clots, anaesthesia-related issues
When Nerve-Sparing Is Not Advisable
- Temporary urinary leakage
- Erectile dysfunction (varies per patient)
- Rare injury to rectum or surrounding tissues
- Infection or bleeding
- Scar tissue formation causing narrowing (stricture)
- Lymphocele formation after lymph node removal
- Very rare: blood clots, anaesthesia-related issues
Book a Consultation
If you or a loved one needs a kidney transplant, consult Dr. Amit Goel, a trusted Urologist & Kidney Transplant Specialist, to discuss robotic or open transplant options and donor procedures.
📍 C2/902, Parsvnath Exotica, DLF Phase 5, Sector 53, Gurugram, Haryana 122003
📞 +91 84470 18167
