Robotic Radical Cystectomy with construction of Total Intracorporeal Orthotopic Ileal Neobladder / Ileal conduit for Cancer Bladder
What Is Robotic Radical Cystectomy?
- A minimally invasive robotic surgery to remove the urinary bladder affected by cancer.
- Performed using the da Vinci Robotic System which provides:
- 3D magnified view
- Wristed, precise instruments
- Tremor-free surgical movements
- 3D magnified view
- Considered the gold standard for muscle-invasive and high-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
- Entire surgery—including bladder removal and urinary diversion—can be done intracorporeally (inside the body).
Why Intracorporeal Urinary Diversion?
After removing the bladder, surgeons create a new path for urine. Robotic surgery allows the entire reconstruction inside the body, leading to:
- Smaller incisions
- Less bowel handling
- Reduced risk of infection
- Faster bowel recovery
- Better cosmesis
- Lower postoperative pain
Two main diversion options:
- Orthotopic Ileal Neobladder (new bladder)
- Ileal Conduit (stoma-based diversion)
Types of Urinary Diversion Explained
A. Orthotopic Ileal Neobladder
- A new bladder constructed from a segment of small intestine.
- Positioned in the same anatomical location as the original bladder.
- Allows:
- Passing urine naturally through the urethra
- Near-normal voiding sensation
- Better quality of life
- Passing urine naturally through the urethra
- Suitable for patients where urethra is cancer-free.
B. Ileal Conduit (Urostomy)
- A segment of ileum is used to create a small tube (conduit).
- Urine is diverted from the kidneys to a stoma on the abdomen.
- Collected in an external urostomy bag.
- Simple, reliable, and preferred for older or high-risk patients.
- A segment of ileum is used to create a small tube (conduit).
Indications for Robotic Radical Cystectomy
- Muscle-invasive bladder cancer (T2 and above).
- High-grade recurrent non-muscle invasive bladder cancer.
- BCG-unresponsive carcinoma in situ (CIS).
- Large tumors occupying the bladder.
- Tumors involving bladder neck or trigone.
- Certain cases of urethral cancer.
Preoperative Evaluation
- MRI / CT scan of abdomen & pelvis.
- Cystoscopy and biopsy.
- Lab tests including kidney function.
- Anaesthesia evaluation.
- Nutritional optimization.
- Bowel preparation as per protocol.
- Counselling about:
- Type of urinary diversion
- Lifestyle changes
- Stoma care (if ileal conduit)
- Continence training (if neobladder)
- Type of urinary diversion
Advantages of Robotic Cystectomy Over Open Surgery
- Better visualization of pelvic structures
- Less blood loss
- Lower transfusion rates
- Reduced bowel dysfunction
- Smaller incision → faster healing
- Lower infection rates
- Shorter hospital stay
- Precise lymph node dissection
- Enhanced recovery and early ambulation
Step-by-Step Surgical Procedure
A. Radical Cystectomy
- Performed under general anaesthesia.
- 5–6 robotic ports placed in the abdomen.
- Key surgical steps:
- Isolation and removal of urinary bladder
- Removal of prostate & seminal vesicles (in males)
- Removal of uterus, ovaries & part of vagina (in females, if required)
- Pelvic lymph node dissection (standard or extended)
- Isolation and removal of urinary bladder
Ensures complete cancer clearance.
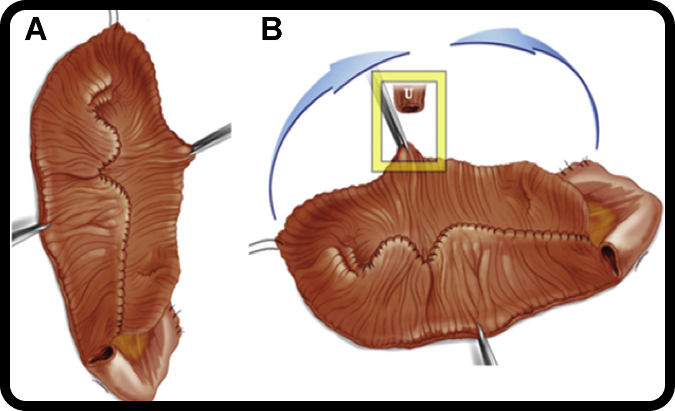
Total Intracorporeal Neobladder Reconstruction (if selected)
- Ileal Segment Selection
- 50–65 cm of terminal ileum isolated for creating neobladder.
- Bowel continuity restored.
- Neobladder Construction Inside the Body
- Ileal segment detubularized and folded into a spherical reservoir.
- Performs similar to a natural bladder.
- Connection to Urethra
- Neobladder is attached to the urethra for natural urine passage.
- Ureter Implantation
- Both ureters implanted into the neobladder.
- Testing & Completion
- Reservoir checked for leaks.
- Catheter and stents placed for temporary drainage.
Total Intracorporeal Ileal Conduit (if selected)
- Ileal Loop Selection
- 15–20 cm of ileum chosen.
- Ureters Connected
- Ureters attached to the ileal conduit (Wallace or Bricker technique).
- Stoma Creation
- A small opening (stoma) created on the abdominal wall.
- Conduit brought out through the stoma.
- Stoma Appliance
External urostomy bag used to collect urine.
Postoperative Recovery
Hospital Stay
- Usually 5–7 days (shorter than open surgery).
Bowel Function
- Faster return due to minimal bowel handling.
Pain
- Mild; managed with oral medications.
Mobility
- Walking encouraged on Day
Diet
- Clear liquids ➝ soft diet ➝ normal diet within days.
Catheters & Stents
- Neobladder: Catheter for 2–3 weeks until healing completes.
- Conduit: Stents removed after 10–14 days.
Long-Term Outcomes
Cancer Control
- Excellent oncological results with high lymph node yield.
- Clear surgical margins leading to improved survival.
Quality of Life
With a neobladder:
- Natural urination through urethra
- No external appliance
- Good daytime continence
- Nighttime continence improves gradually
With an ileal conduit:
- Reliable urinary diversion
- Low complication rates
- Easy stoma care
- Suitable for older / frail patients
Possible Risks & Complications
Short Term
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Bowel obstruction
- Lymphocele
- Urine leak
Long Term
- Neobladder:
- Continence issues (temporary)
- Mucus production
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Metabolic acidosis (rare)
- Continence issues (temporary)
- Ileal Conduit:
- Stoma-related issues
- Appliance leakage
- Skin irritation
- Robotic approach significantly reduces complication rates.
- Stoma-related issues
Who Is a Candidate for Neobladder vs. Ileal Conduit?
Orthotopic Neobladder Ideal For:
- Younger patients (<70 years)
- Good kidney function
- Good urethral function
- Cancer not involving the urethra
- Motivated for neobladder training
Ileal Conduit Ideal For:
- Older / medically complex patients
- Poor kidney function
- Prior pelvic radiation
- Urethral involvement
- Want simplest diversion method
Book a Consultation
If you or a loved one needs a kidney transplant, consult Dr. Amit Goel, a trusted Urologist & Kidney Transplant Specialist, to discuss robotic or open transplant options and donor procedures.
📍 C2/902, Parsvnath Exotica, DLF Phase 5, Sector 53, Gurugram, Haryana 122003
📞 +91 84470 18167
